(1) Next_permutation 함수란?
범위의 요소를 [first,last]다음 사전 식으로더 큰 순열로 다시 정렬합니다.
ex) 1,2,3 -> 1,3,2 -> 2,1,3 -> 2,3,1 -> 3,1,2 -> 3,2,1
단, 1,3,2 에서 시작 시 1,2,3의 경우는 돌아가지 않는다.
(2) Next_permutation 함수 구조
- 필요 헤더
#include <algorithm>
- 템플릿
//default
template <class BidirectionalIterator>
bool next_permutation (BidirectionalIterator first,
BidirectionalIterator last);
//custom(비교문을 넣을 수 있음)
template <class BidirectionalIterator, class Compare>
bool next_permutation (BidirectionalIterator first,
BidirectionalIterator last, Compare comp);
<------------------------예제------------------------>
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <algorithm> // std::next_permutation, std::sort
int main () {
int myints[] = {1,2,3};
std::sort (myints,myints+3);
std::cout << "The 3! possible permutations with 3 elements:\n";
do {
std::cout << myints[0] << ' ' << myints[1] << ' ' << myints[2] << '\n';
} while ( std::next_permutation(myints,myints+3) );
std::cout << "After loop: " << myints[0] << ' ' << myints[1] << ' ' << myints[2] << '\n';
return 0;
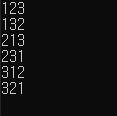
}(3) Next_permutation 사용법
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(3);
//모든 경우의 수를 확인하기 위해 최초 벡터를 오름차순으로 정렬
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
do {
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
cout << v.at(i);
}
cout << endl;
} while (next_permutation(v.begin(), v.end()));
return 0;
}
아래 링크를 통해 Next_permutation 함수를 사용한 완전탐색예제를 확인하실수 있습니다.
2020/11/27 - [Programmers/C++] - [프로그래머스] 코딩테스트 연습 > 완전탐색 > 소수 찾기(C++)
'Study > C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [TCP] TCP - Server (2) | 2020.11.06 |
|---|---|
| [STL] Vector Container 기본 사용법 (0) | 2020.10.21 |

